The Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Worksheet Answers provide a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental processes of cellular respiration. This guide delves into the intricate details of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, equipping readers with a thorough knowledge of their mechanisms, applications, and implications.
This document offers a comprehensive overview of the topic, covering the processes, organisms involved, and the comparison between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Additionally, it explores the industrial, environmental, and medical applications of these processes.
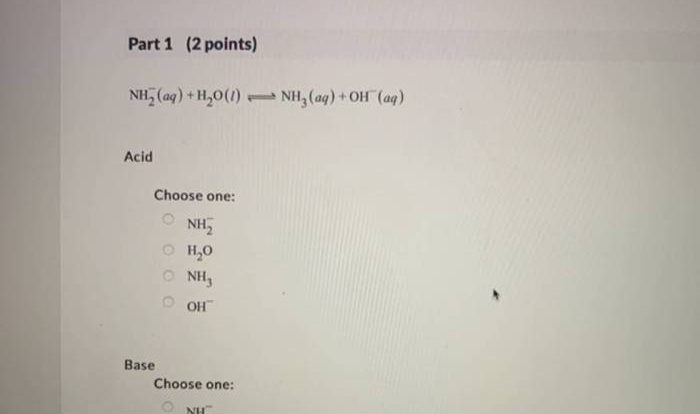
Aerobic Respiration
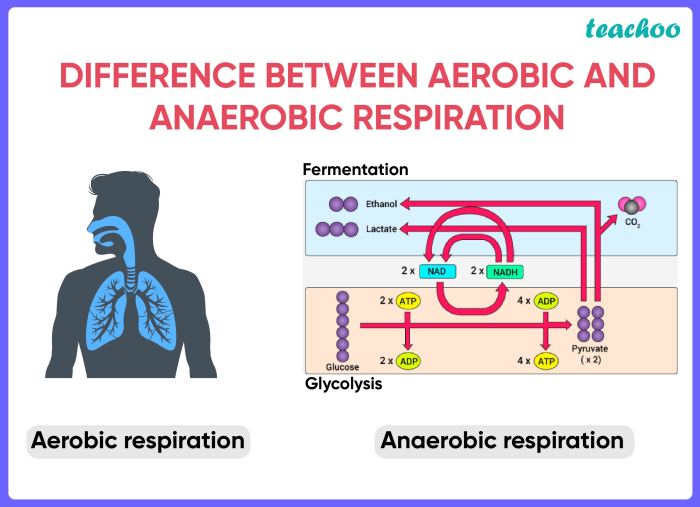
Aerobic respiration is a metabolic process that utilizes oxygen to generate energy for cellular activities. It occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and involves the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar molecule, into carbon dioxide and water.
Steps Involved in Aerobic Respiration, Aerobic and anaerobic respiration worksheet answers
- Glycolysis:Glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules in the cytoplasm.
- Pyruvate Oxidation:Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA and carbon dioxide in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle):Acetyl-CoA enters a series of reactions that generate carbon dioxide, NADH, and FADH2.
- Electron Transport Chain:NADH and FADH2 pass electrons through a series of protein complexes, pumping protons across the mitochondrial membrane and generating ATP.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation:Protons flow back across the mitochondrial membrane through ATP synthase, synthesizing ATP.
Organisms that Undergo Aerobic Respiration
- Humans
- Animals
- Plants (during the day)
Anaerobic Respiration: Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration Worksheet Answers

Anaerobic respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in the absence of oxygen and generates energy by breaking down organic compounds, such as glucose. It occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and produces less energy compared to aerobic respiration.
Steps Involved in Anaerobic Respiration
- Glycolysis:Glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules in the cytoplasm.
- Lactate Fermentation:Pyruvate is converted into lactate in animals, while in plants and some microorganisms, it is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Organisms that Undergo Anaerobic Respiration
- Humans (during intense exercise)
- Yeast
- Bacteria
Comparison of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration | |
|---|---|---|
| Products | Carbon dioxide, water | Lactate (animals), ethanol and carbon dioxide (plants and microorganisms) |
| Energy Yield | 36-38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule | 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule |
| Oxygen Requirement | Requires oxygen | Does not require oxygen |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | High energy yield | Can occur in the absence of oxygen |
| Disadvantages | Requires oxygen | Low energy yield |
Applications of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Industrial Applications
- Aerobic respiration:Food processing, waste treatment, production of antibiotics and enzymes
- Anaerobic respiration:Production of biofuels (e.g., ethanol), production of biogas
Environmental Implications
- Aerobic respiration:Oxygen consumption can contribute to climate change
- Anaerobic respiration:Can produce methane, a greenhouse gas
Medical Applications
- Aerobic respiration:Understanding energy metabolism in cells can help diagnose and treat diseases
- Anaerobic respiration:Used in sports medicine to improve performance and recovery
FAQ Summary
What is the primary difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not.
Which organisms undergo anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is commonly found in microorganisms such as yeast and bacteria.
What is the significance of the Krebs cycle in aerobic respiration?
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that generate energy-rich molecules during aerobic respiration.