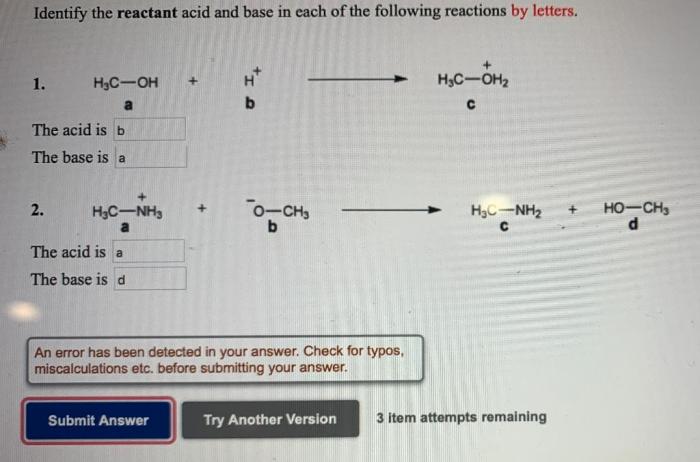
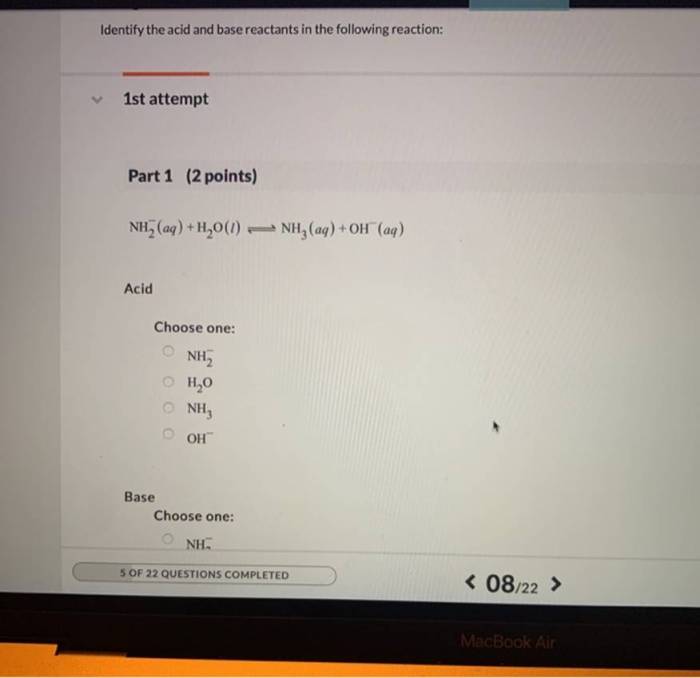
Identify the acid and base reactants in the following reaction – Identifying acid and base reactants is a fundamental aspect of chemistry. Acids and bases play crucial roles in various chemical reactions, and understanding their properties and behavior is essential for comprehending the mechanisms of these reactions.
This guide will delve into the concept of acids and bases, exploring their properties, strength, and applications in different fields. We will also discuss the types of acid-base reactions and their significance in everyday life and industrial processes.
Identify Acid and Base Reactants
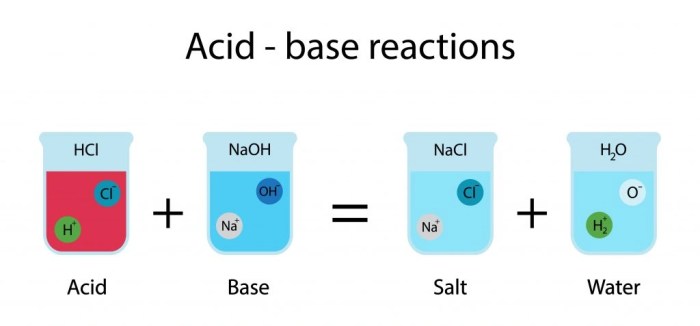
Acids and bases are two fundamental concepts in chemistry. Acids are substances that donate protons (H+), while bases are substances that accept protons. The strength of an acid or base is determined by its ability to donate or accept protons.
Examples of Acids and Bases
- Strong acids: Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3)
- Weak acids: Acetic acid (CH3COOH), carbonic acid (H2CO3), phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
- Strong bases: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
- Weak bases: Ammonia (NH3), pyridine (C5H5N), sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases have distinct properties that allow them to be identified and distinguished. Acids are typically sour to taste, turn blue litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases are typically bitter to taste, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to produce water and a salt.
Reaction Types
Acids and bases can undergo a variety of reactions, including:
Neutralization Reactions
Neutralization reactions occur when an acid and a base react in stoichiometric proportions to produce a salt and water. The salt is formed by the exchange of the hydrogen ion from the acid with the hydroxide ion from the base.
Acid-Base Titrations
Acid-base titrations are used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. A known volume of the unknown solution is titrated with a solution of known concentration until the equivalence point is reached. The equivalence point is the point at which the moles of acid are equal to the moles of base.
Precipitation Reactions, Identify the acid and base reactants in the following reaction
Precipitation reactions occur when two solutions containing ions react to form an insoluble solid precipitate. The precipitate is formed by the combination of the positive and negative ions in the solutions.
Acid-Base Strength
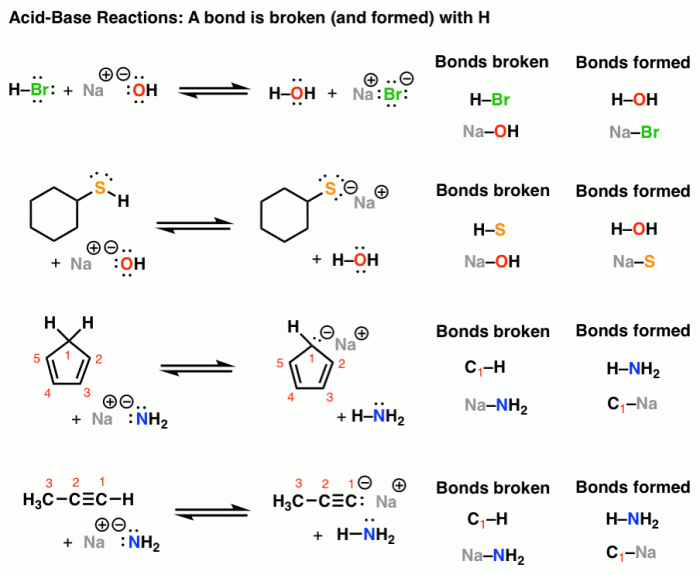
The strength of an acid or base is determined by its ability to donate or accept protons. The stronger the acid, the more readily it donates protons. The stronger the base, the more readily it accepts protons.
Factors Affecting Acid-Base Strength
- Electronegativity: The more electronegative the atom that the proton is attached to, the stronger the acid.
- Bond length: The shorter the bond length between the proton and the atom that it is attached to, the stronger the acid.
- Resonance: Resonance can stabilize the conjugate base of an acid, making the acid weaker.
- Solvation: Solvation of the conjugate base can also stabilize the acid, making it weaker.
Relationship between Acid-Base Strength and Reaction Rates
The strength of an acid or base has a significant impact on the rate of reaction. In general, stronger acids and bases react more quickly than weaker acids and bases.
Applications of Acid-Base Reactions: Identify The Acid And Base Reactants In The Following Reaction
Acid-base reactions have a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life.
Industrial Applications
- Production of fertilizers
- Petroleum refining
- Manufacture of paper
- Textile dyeing
- Food processing
Everyday Life Applications
- Batteries
- Antacids
- Cleaning products
- Water treatment
- Food preservation
Environmental Implications
Acid-base reactions can have a significant impact on the environment. Acid rain, which is caused by the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, can damage forests, lakes, and buildings. Acidic runoff from mines can also pollute rivers and streams.
Q&A
What are the key properties of acids?
Acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions) in aqueous solutions, turning blue litmus red and sour to taste.
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
Strong acids completely dissociate in water, releasing all their protons, while weak acids only partially dissociate.
What are some common applications of acid-base reactions?
Acid-base reactions are used in various industries, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and metalworking.







