An oligarchy can be like a dictatorship. – An oligarchy, a government ruled by a small elite, can often resemble a dictatorship in its oppressive nature. This essay will delve into the striking similarities between these two forms of governance, exploring their power structures, decision-making processes, and the impact on civil liberties and human rights.
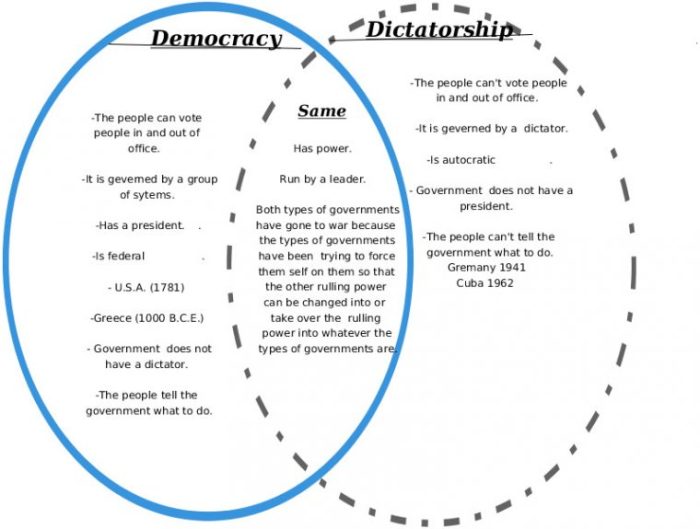
Oligarchies and dictatorships share a common thread: the concentration of power in the hands of a privileged few. In both systems, the elite or the dictator wield immense authority, controlling decision-making and suppressing dissent.
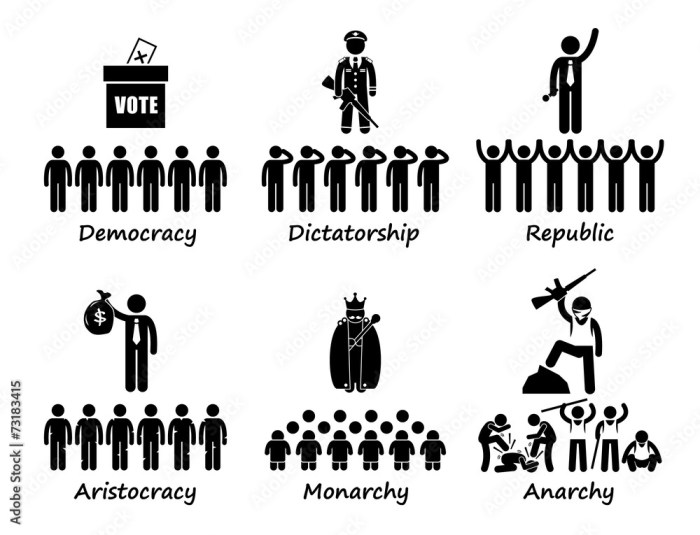
Definitions and Characteristics: An Oligarchy Can Be Like A Dictatorship.

An oligarchy is a form of government in which power is concentrated in the hands of a small group of individuals. This group is typically composed of the wealthy, powerful, and influential members of society. In contrast, a dictatorship is a form of government in which power is concentrated in the hands of a single individual, known as the dictator.
Dictators typically come to power through force or intimidation and rule with absolute authority.
Both oligarchies and dictatorships are characterized by a lack of political participation and accountability. In an oligarchy, the ruling elite is not accountable to the people, and their decisions are often made in secret. In a dictatorship, the dictator is not accountable to anyone and has absolute power over the country.
Power Structure
In an oligarchy, power is concentrated in the hands of a small group of individuals. This group is typically composed of the wealthy, powerful, and influential members of society. Oligarchs may come from a variety of backgrounds, but they all share a common interest in maintaining their power and privilege.
In a dictatorship, power is concentrated in the hands of a single individual, known as the dictator. Dictators typically come to power through force or intimidation and rule with absolute authority. Dictators may be supported by a small group of loyalists, but they are ultimately responsible for all decisions made by the government.
Decision-Making Process
In an oligarchy, decisions are typically made by the ruling elite in secret. The people have no say in the decision-making process, and they are often unaware of the decisions that are being made on their behalf.
In a dictatorship, decisions are made by the dictator. The dictator is not accountable to anyone and has absolute power over the country. The people have no say in the decision-making process, and they are often unaware of the decisions that are being made on their behalf.
Civil Liberties and Human Rights
In an oligarchy, civil liberties and human rights are often restricted. The ruling elite may use their power to suppress dissent and silence their critics. The people may be denied basic rights such as freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom of the press.
In a dictatorship, civil liberties and human rights are often severely restricted. The dictator may use their power to suppress dissent and silence their critics. The people may be denied basic rights such as freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom of the press.
Dictatorships may also use torture, arbitrary arrest, and other forms of human rights abuses to maintain their power.
Economic Systems
Oligarchies and dictatorships are often associated with different economic systems. Oligarchies are typically associated with capitalism, while dictatorships are typically associated with socialism or communism. However, there are many exceptions to this rule. For example, some oligarchies have adopted socialist or communist economic policies, while some dictatorships have adopted capitalist economic policies.
The economic system of a country can have a significant impact on the distribution of wealth and resources. In oligarchies, the wealthy elite often control a large share of the country’s wealth and resources. In dictatorships, the dictator and their loyalists often control a large share of the country’s wealth and resources.
Historical Examples, An oligarchy can be like a dictatorship.
There are many historical examples of oligarchies and dictatorships. Some of the most well-known examples include:
- The Roman Republic was an oligarchy that was ruled by a small group of wealthy and powerful families.
- The Soviet Union was a dictatorship that was ruled by Joseph Stalin.
- Nazi Germany was a dictatorship that was ruled by Adolf Hitler.
- China is a dictatorship that is ruled by the Chinese Communist Party.
These are just a few examples of the many oligarchies and dictatorships that have existed throughout history.
FAQ Resource
What is the key difference between an oligarchy and a dictatorship?
While both concentrate power in the hands of a few, an oligarchy is ruled by a small elite group, whereas a dictatorship is ruled by a single individual.
How do oligarchies impact economic systems?
Oligarchies often lead to wealth inequality, as the elite control access to resources and opportunities.
What are the historical examples of oligarchies?
Ancient Greece, the Roman Republic, and 19th-century United States are examples of oligarchic governments.