Intro to quantum mechanics griffiths pdf – Griffiths’ “Introduction to Quantum Mechanics” PDF provides a comprehensive and engaging exploration into the fundamentals of quantum mechanics, offering a clear understanding of the historical development, fundamental concepts, and practical applications of this captivating field.
Delving into the Schrödinger equation, the structure and energy levels of the hydrogen atom, angular momentum, spin, and approximation methods, this resource equips readers with a solid foundation in quantum mechanics, empowering them to navigate the complexities of this fascinating discipline.
Introduction
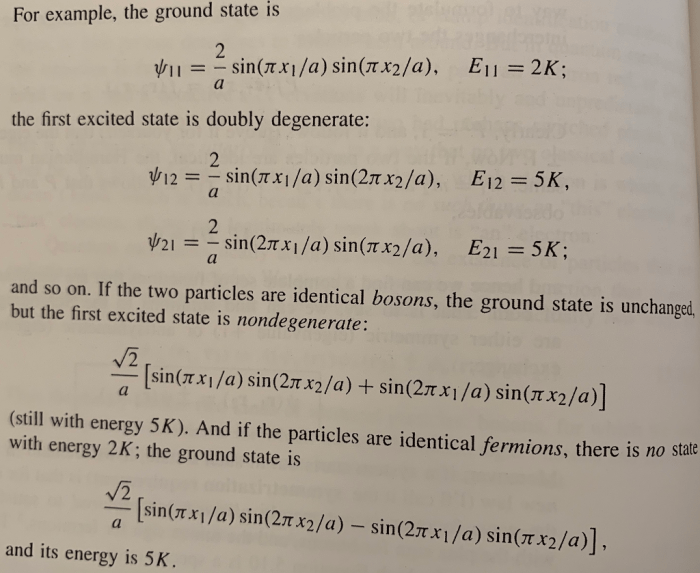
Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter at the atomic and subatomic level. It is based on the idea that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities are quantized, meaning they can only exist in discrete values.
Quantum mechanics was developed in the early 20th century by a number of physicists, including Max Planck, Albert Einstein, Niels Bohr, and Erwin Schrödinger. It has since become one of the most important and successful theories in physics, and has led to the development of many new technologies, including lasers, transistors, and nuclear weapons.
The Schrödinger Equation
The Schrödinger equation is a differential equation that describes the wave function of a quantum mechanical system. The wave function is a mathematical function that contains all of the information about the system, including its energy, momentum, and angular momentum.
The Schrödinger equation can be used to solve for the wave function of a system, and thus to determine its properties. It is a very powerful tool, and has been used to make many important predictions about the behavior of quantum mechanical systems.
The Hydrogen Atom

The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and it is therefore a good system to study quantum mechanics. The hydrogen atom consists of a single proton and a single electron.
The Schrödinger equation can be used to solve for the wave function of the hydrogen atom, and thus to determine its energy levels. The energy levels of the hydrogen atom are quantized, and they correspond to the different energy states of the electron.
Angular Momentum

Angular momentum is a measure of the amount of rotation of a system. It is a vector quantity, and it has both a magnitude and a direction.
Angular momentum is quantized, and it can only exist in discrete values. The magnitude of the angular momentum of a system is given by the following equation:
$$\textAngular Momentum=\sqrtl(l+1)\hbar$$
where $l$ is the angular momentum quantum number and $\hbar$ is the reduced Planck constant.
Spin
Spin is a type of angular momentum that is intrinsic to elementary particles. It is a vector quantity, and it has both a magnitude and a direction.
Spin is quantized, and it can only exist in discrete values. The magnitude of the spin of an elementary particle is given by the following equation:
$$\textSpin=\sqrts(s+1)\hbar$$
where $s$ is the spin quantum number and $\hbar$ is the reduced Planck constant.
Identical Particles
Identical particles are particles that have the same mass, charge, and spin. They are indistinguishable from each other, and they must be treated in a symmetric way.
The wave function of a system of identical particles must be either symmetric or antisymmetric under the exchange of any two particles.
Approximation Methods
Quantum mechanics is a very complex theory, and it is often difficult to solve the Schrödinger equation exactly. There are a number of approximation methods that can be used to simplify the problem.
One of the most common approximation methods is the variational method. The variational method involves finding a trial wave function that is as close as possible to the exact wave function. The energy of the system can then be calculated using the trial wave function.
Applications of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics has a wide range of applications in different fields, including physics, chemistry, and biology.
In physics, quantum mechanics is used to explain the behavior of atoms, molecules, and other subatomic particles. It is also used to develop new technologies, such as lasers and transistors.
In chemistry, quantum mechanics is used to study the structure and bonding of molecules. It is also used to develop new drugs and materials.
In biology, quantum mechanics is used to study the structure and function of proteins and other biological molecules. It is also used to develop new medical treatments.
Answers to Common Questions: Intro To Quantum Mechanics Griffiths Pdf
Where can I find Griffiths’ “Introduction to Quantum Mechanics” PDF?
The PDF can be accessed through various online platforms, including university libraries, academic databases, and the publisher’s website.
Is Griffiths’ textbook suitable for beginners in quantum mechanics?
Yes, Griffiths’ textbook is widely regarded as an accessible and comprehensive introduction to quantum mechanics, making it suitable for both beginners and students with some prior knowledge in physics.
What are the key concepts covered in Griffiths’ textbook?
Griffiths’ textbook covers a wide range of topics in quantum mechanics, including the Schrödinger equation, the hydrogen atom, angular momentum, spin, identical particles, and approximation methods.