Aquatic ecosystems worksheet answer key – Delve into the depths of aquatic ecosystems with our comprehensive worksheet answer key, a treasure trove of knowledge that unlocks the mysteries of these vibrant underwater worlds. Dive into the intricate web of life, explore the delicate balance of abiotic and biotic components, and uncover the threats that imperil these aquatic havens.
Our answer key not only provides accurate solutions but also embarks on a captivating journey, weaving together scientific insights with real-world examples. Prepare to be enthralled as we navigate the complexities of aquatic ecosystems, unravel their ecological significance, and empower you with the knowledge to safeguard these precious resources.
Aquatic Ecosystems: A Vital Part of the Global Ecosystem
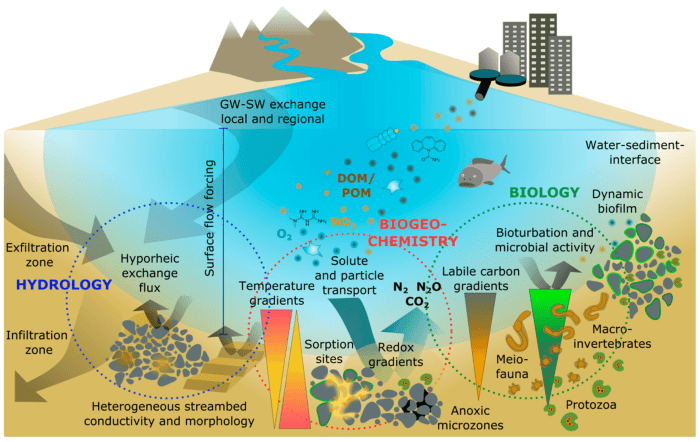
Aquatic ecosystems are bodies of water that support a wide range of life forms and play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the planet.
Key Concepts
Aquatic ecosystems encompass all water bodies, from the smallest ponds to the vast oceans. They are characterized by their unique physical and chemical properties, such as temperature, salinity, and dissolved oxygen levels, which influence the types of organisms that can survive in them.
Types of Aquatic Ecosystems
- Freshwater ecosystems: These include lakes, rivers, streams, and wetlands. They are characterized by low salinity and relatively high levels of dissolved oxygen.
- Marine ecosystems: These include oceans, seas, and estuaries. They are characterized by high salinity and relatively low levels of dissolved oxygen.
Components of Aquatic Ecosystems, Aquatic ecosystems worksheet answer key
Biotic Components
- Producers: These are organisms that can convert inorganic matter into organic matter through photosynthesis. They include phytoplankton, algae, and aquatic plants.
- Consumers: These are organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms to obtain energy. They include zooplankton, fish, and marine mammals.
- Decomposers: These are organisms that break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. They include bacteria and fungi.
Abiotic Components
- Water: Water is the primary component of aquatic ecosystems and provides a habitat for aquatic organisms.
- Temperature: Temperature influences the distribution and abundance of aquatic organisms.
- Light: Light is essential for photosynthesis and affects the growth and distribution of aquatic plants.
- Nutrients: Nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are essential for the growth of aquatic organisms.
Interrelationships Between Biotic and Abiotic Components
The biotic and abiotic components of aquatic ecosystems are closely interconnected and interdependent. For example, the availability of light affects the growth of aquatic plants, which in turn provides food and shelter for aquatic animals.
Essential Questionnaire: Aquatic Ecosystems Worksheet Answer Key
What are the key threats facing aquatic ecosystems?
Pollution, overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change pose significant threats to aquatic ecosystems.
How can we mitigate these threats?
Implementing pollution control measures, regulating fishing practices, protecting and restoring habitats, and reducing carbon emissions are crucial steps in mitigating threats to aquatic ecosystems.
Why are aquatic ecosystems important?
Aquatic ecosystems provide essential ecological services, including nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and support for fisheries and tourism.