Energy flow in the ecosystem worksheet introduces a fundamental concept that underpins the intricate web of life. This comprehensive guide delves into the mechanisms by which energy is captured, transferred, and utilized within ecosystems, providing a deeper understanding of the delicate balance that sustains our planet.
Through detailed explanations, engaging examples, and insightful discussions, this worksheet unravels the intricate tapestry of energy flow, empowering readers with a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.
Introduction
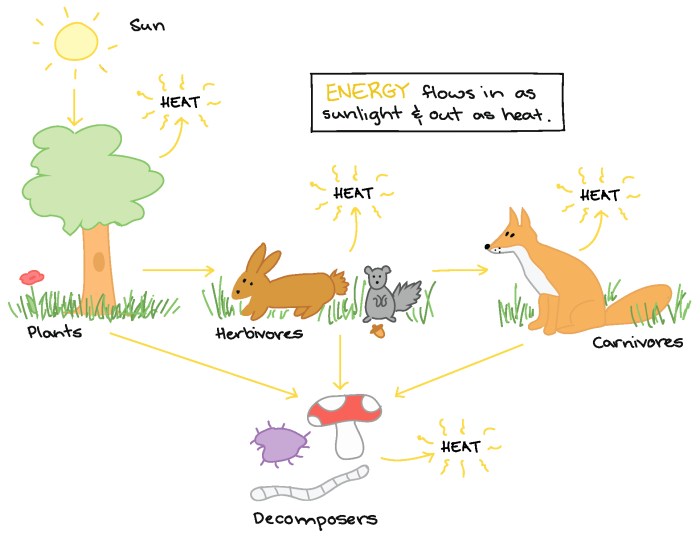
Energy flow is the transfer of energy from one organism to another within an ecosystem. It is a fundamental process that drives the functioning of all ecosystems, providing the energy necessary for organisms to survive and reproduce.
Producers and Consumers
Producers are organisms that capture energy from the sun through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy stored in organic molecules. Consumers are organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms to obtain energy.
Types of Consumers
- Herbivores: Feed on plants
- Carnivores: Feed on animals
- Omnivores: Feed on both plants and animals
- Decomposers: Break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients
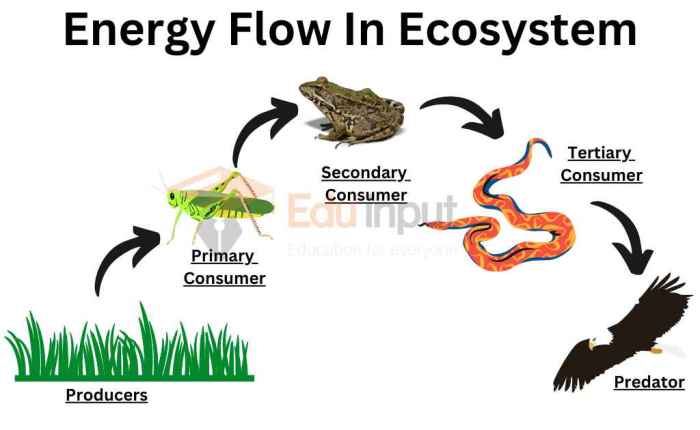
Trophic Levels: Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Worksheet
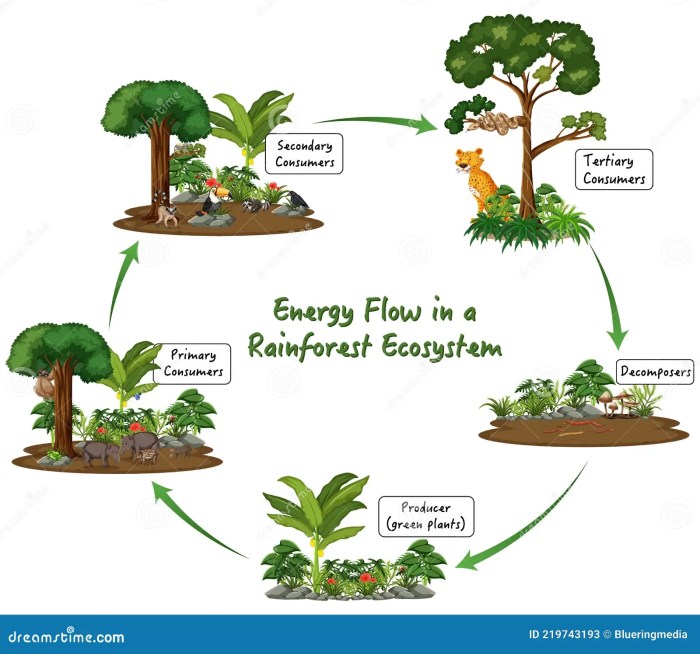
Trophic levels represent the different stages of energy transfer within an ecosystem. Each trophic level is occupied by organisms that share a similar feeding relationship.
Diagram of Trophic Levels
| Trophic Level | Organisms |
|---|---|
| Producers | Plants |
| Primary Consumers (Herbivores) | Rabbits |
| Secondary Consumers (Carnivores) | Foxes |
| Tertiary Consumers (Top Predators) | Lions |
Food Webs and Food Chains
Food webs are interconnected food chains that represent the feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Food chains are linear sequences of organisms, each feeding on the one below it.
Examples of Food Webs and Food Chains
- Grassland food web: Grass → Grasshopper → Mouse → Owl
- Ocean food chain: Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Fish → Shark
Energy Pyramids
Energy pyramids are graphical representations that show the amount of energy available at each trophic level in an ecosystem. They demonstrate the loss of energy as it flows through the ecosystem.
Diagram of an Energy Pyramid
[Diagram menunjukkan piramida dengan level trofik di sepanjang sumbu x dan energi yang tersedia di sumbu y, menunjukkan penurunan energi di setiap level]
Human Impact on Energy Flow
Human activities can significantly affect energy flow in ecosystems. These include:
- Habitat destruction
- Pollution
- Climate change
Consequences of Human Impact, Energy flow in the ecosystem worksheet
- Reduced biodiversity
- Disruption of food webs
- Altered ecosystem functioning
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of energy flow in ecosystems?
Energy flow is crucial for the functioning of ecosystems as it provides the energy necessary for organisms to carry out essential life processes, such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient cycling.
How do producers and consumers contribute to energy flow?
Producers, such as plants, capture energy from the sun through photosynthesis, while consumers, such as animals, obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
What are trophic levels and how do they relate to energy flow?
Trophic levels represent the different stages of energy transfer within an ecosystem. Energy flows from producers to primary consumers, then to secondary consumers, and so on.
How do food webs and food chains illustrate energy flow?
Food webs and food chains depict the interconnected feeding relationships between organisms, highlighting the pathways through which energy is transferred within ecosystems.
What are the consequences of human impact on energy flow?
Human activities, such as habitat destruction and pollution, can disrupt energy flow in ecosystems, leading to imbalances and potential ecosystem collapse.