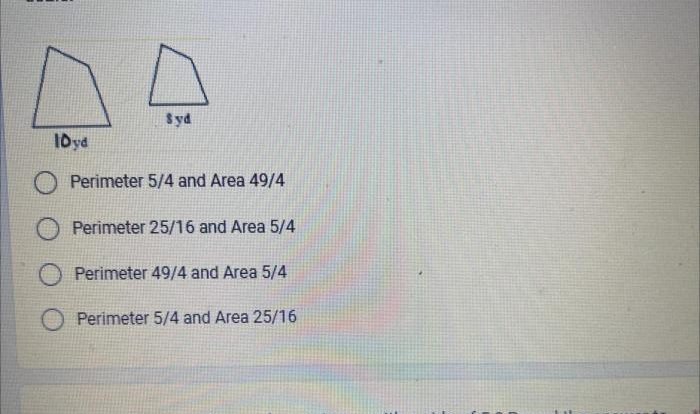
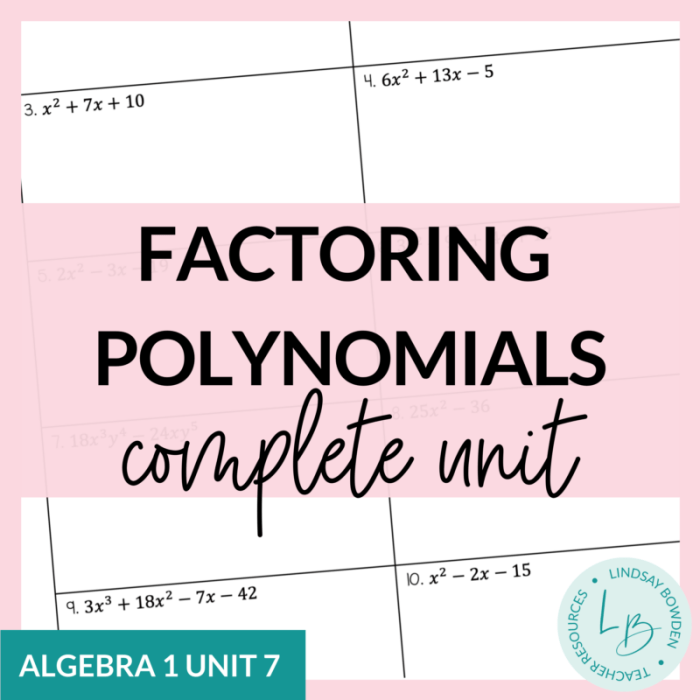
Polynomials and factoring unit test, a comprehensive assessment tool, delves into the intricacies of polynomials, their types, and the techniques employed in factoring them. This engaging exploration unveils the fundamental concepts, strategies, and applications of polynomials, empowering students with a thorough understanding of this critical mathematical domain.
Polynomials, ubiquitous in various scientific and engineering disciplines, provide a potent tool for modeling complex phenomena. Factoring, a technique central to polynomial manipulation, enables the decomposition of polynomials into simpler components, facilitating problem-solving and revealing hidden insights.
Introduction

Polynomials are algebraic expressions consisting of variables and coefficients, combined using mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Factoring involves expressing a polynomial as a product of simpler polynomials. A unit test is a crucial assessment tool designed to evaluate students’ understanding of a specific topic, such as polynomials and factoring.
Purpose of a Unit Test
Unit tests serve multiple purposes. They assess students’ comprehension of the concepts and skills covered in a particular unit, identify areas where students need additional support, provide feedback to students and instructors on learning progress, and contribute to students’ overall grades.
In the context of polynomials and factoring, a unit test typically includes questions that test students’ ability to:
- Identify and classify polynomials
- Perform basic polynomial operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication)
- Factor polynomials using various methods (e.g., common factors, grouping, difference of squares)
- Solve polynomial equations
By taking a unit test, students can demonstrate their proficiency in these concepts and receive valuable feedback on their strengths and weaknesses.
Types of Polynomials
Polynomials are mathematical expressions consisting of variables and coefficients. They can be classified into different types based on the number of terms they contain.
Monomials
Monomials are polynomials with only one term. They are composed of a single variable raised to a non-negative integer power.
- Example: 3x
Binomials
Binomials are polynomials with two terms. They are typically written as a sum or difference of two monomials.
- Example: x + 2
- Example: 3y – 5
Trinomials
Trinomials are polynomials with three terms. They are typically written as a sum or difference of three monomials.
- Example: x 2+ 2x + 1
- Example: 3y 2– 5y + 2
Factoring Polynomials: Polynomials And Factoring Unit Test
Factoring polynomials involves expressing a polynomial as a product of smaller polynomials, also known as factors. This process is essential in solving polynomial equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding the behavior of polynomials. Various methods exist for factoring polynomials, each with its own advantages and applicability.
Factoring by Grouping
This method is useful when the polynomial has four terms that can be grouped into two pairs of binomials.Steps:
- Group the first two and last two terms together.
- Factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each group.
- Combine the two factors by using the distributive property.
For example, to factor 2x^2 + 5x
- 3x
- 15, we can group the terms as (2x^2 + 5x) and (-3x
- 15), factor out the GCF (x and
-3), and combine to get
(x)(2x + 5)
- 3(x + 5) = (x
- 3)(2x + 5)
Factoring by Substitution
This method is effective when the polynomial is a quadratic trinomial that can be written in the form ax^2 + bx + c.Steps:
- Let u = x + k, where k is a constant to be determined.
- Substitute u into the polynomial and simplify.
- Factor the resulting quadratic trinomial in u.
- Replace u with x + k to obtain the factors of the original polynomial.
For example, to factor x^2 + 5x + 6, we can let u = x + 2 and substitute:(u
- 2)^2 + 5(u
- 2) + 6 = u^2
- 4u + 4 + 5u
- 10 + 6 = u^2 + u
- 10
Factoring the quadratic trinomial in u, we get:(u + 5)(u
2)
Replacing u with x + 2, we obtain the factors of the original polynomial:(x + 5)(x + 2)
Polynomial Unit Test

A unit test on polynomials and factoring should assess students’ understanding of the following key concepts:
Polynomials and their properties
- Degree of a polynomial
- Leading coefficient
- Constant term
- End behavior
Factoring polynomials
- Common factors
- Difference of squares
- Perfect square trinomials
- Trinomials of the form $ax^2+bx+c$
Solving polynomial equations
- Setting a polynomial equal to zero
- Using factoring to find solutions
- Using the quadratic formula
Sample Questions
- Find the degree and leading coefficient of the polynomial $3x^4-2x^3+5x^2-1$
- Factor the polynomial $x^2-9$
- Solve the polynomial equation $x^2-5x+6=0$
Study Tips for Polynomials and Factoring
Mastering polynomials and factoring requires effective study strategies. This section provides valuable tips to enhance your understanding and proficiency in these concepts.
Memorizing Formulas
Polynomials and factoring involve numerous formulas. To memorize them effectively:
- Understand the concepts behind each formula.
- Practice applying formulas in various scenarios.
- Use flashcards or create a formula sheet for quick reference.
Practicing Factoring Skills
Factoring polynomials requires practice and repetition. Here are some tips:
- Start with simple polynomials and gradually increase the complexity.
- Break down factoring problems into smaller steps.
- Use factoring techniques such as the zero product property, grouping, and factoring by substitution.
- Check your answers by multiplying the factors.
Real-World Applications of Polynomials and Factoring
Polynomials and factoring are powerful mathematical tools with a wide range of applications in various fields. They provide a means to model and solve complex problems in science, engineering, finance, and many other areas.
Science, Polynomials and factoring unit test
- Physics:Polynomials are used to describe the motion of objects, such as projectiles and satellites, using equations of motion and trajectory analysis.
- Chemistry:Factoring is used to balance chemical equations and determine the stoichiometry of reactions.
- Biology:Polynomials can model population growth, disease spread, and genetic inheritance.
Engineering
- Civil Engineering:Polynomials are used to design structures, such as bridges and buildings, by calculating forces and stresses.
- Mechanical Engineering:Factoring is used to analyze vibrations and oscillations in mechanical systems.
- Electrical Engineering:Polynomials are used to model electrical circuits and design filters and amplifiers.
Finance
- Investment Analysis:Polynomials are used to model stock prices and predict future trends.
- Risk Management:Factoring is used to evaluate the risk of financial instruments and portfolios.
- Loan Amortization:Polynomials are used to calculate loan payments and determine the amortization schedule.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the different types of polynomials?
Polynomials are classified based on the number of terms they contain: monomials (one term), binomials (two terms), trinomials (three terms), and so on.
What is the purpose of factoring polynomials?
Factoring polynomials simplifies their form, reveals their structure, and facilitates solving polynomial equations and inequalities.
What are the key concepts tested in a polynomials and factoring unit test?
Unit tests typically assess students’ understanding of polynomial types, factoring methods (e.g., grouping, substitution), polynomial operations, and applications.