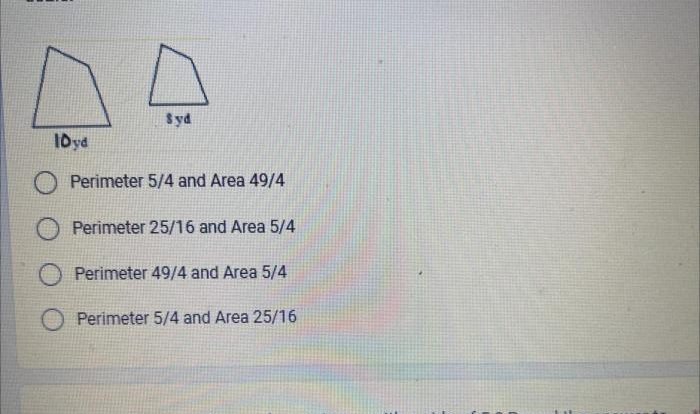
Discover the fascinating world of weather observation with our comprehensive gizmos observing weather answer key. This guide unlocks the mysteries of meteorology, empowering you with a profound understanding of weather patterns and their impact on our lives.
Delving into the intricacies of weather gizmos, we explore their diverse types, functions, and applications. From the humble barometer to the sophisticated Doppler radar, each gizmo plays a crucial role in collecting and interpreting weather data, enabling us to predict and prepare for atmospheric changes.
Introduction
Weather observation is the systematic collection and analysis of weather data, which provides valuable information about the current and future state of the atmosphere. Understanding weather patterns is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, transportation, and disaster management.
Gizmo refers to a simple device or apparatus used for scientific observation and experimentation. In the context of weather observation, gizmos are used to measure and record various atmospheric parameters, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and direction.
Role of Gizmos in Weather Observation
- Temperature Measurement: Gizmos like thermometers measure air temperature, which is essential for understanding temperature variations and forecasting weather conditions.
- Humidity Measurement: Hygrometers measure the amount of water vapor in the air, which helps determine the likelihood of precipitation and cloud formation.
- Wind Speed and Direction Measurement: Anemometers and wind vanes measure wind speed and direction, respectively, providing insights into wind patterns and potential storm development.
- Barometric Pressure Measurement: Barometers measure atmospheric pressure, which can indicate changes in weather conditions and predict approaching storms.
Types of Weather Gizmos
Weather gizmos are instruments used to measure and monitor various aspects of the weather. They come in different types, each designed to measure specific weather parameters. Understanding the principles behind their operation and the accuracy, cost, and ease of use of different types of weather gizmos is essential for selecting the appropriate tool for specific weather monitoring needs.
Common Weather Gizmos
- Thermometer:Measures temperature using the expansion and contraction of a liquid or gas.
- Barometer:Measures atmospheric pressure using a column of liquid, typically mercury or water.
- Anemometer:Measures wind speed using rotating cups or a propeller.
- Rain Gauge:Measures precipitation by collecting rainwater in a funnel and measuring its volume.
- Hygrometer:Measures humidity by measuring the amount of water vapor in the air.
Comparison of Weather Gizmos, Gizmos observing weather answer key
The following table compares different types of weather gizmos based on their accuracy, cost, and ease of use:
| Gizmo | Accuracy | Cost | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermometer | Varies depending on type | Low to moderate | Easy |
| Barometer | High | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Anemometer | Moderate to high | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Rain Gauge | Moderate | Low to moderate | Easy |
| Hygrometer | Moderate | Low to moderate | Easy |
The accuracy of a weather gizmo depends on its design and calibration. Cost can vary depending on the features and materials used. Ease of use refers to how simple it is to operate and interpret the measurements.
Applications of Weather Gizmos
Weather gizmos are widely employed in various fields, offering invaluable insights into weather patterns and contributing to critical decision-making processes.
Meteorologists rely on weather gizmos to gather real-time data on atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, and precipitation. This information is essential for weather forecasting, enabling meteorologists to predict upcoming weather patterns and issue timely warnings and advisories.
Aviation
In the aviation industry, weather gizmos play a crucial role in ensuring flight safety and efficiency. Pilots utilize weather gizmos to obtain accurate weather information along their flight paths, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding takeoff, landing, and route selection.
By avoiding adverse weather conditions, airlines can minimize flight delays, optimize fuel consumption, and enhance passenger safety.
Agriculture
Weather gizmos are indispensable tools for farmers and agriculturalists. By monitoring weather conditions, farmers can optimize crop management practices, such as irrigation scheduling, pest control, and harvesting. Weather gizmos provide insights into temperature fluctuations, precipitation patterns, and wind conditions, enabling farmers to make informed decisions that maximize crop yields and minimize losses due to weather-related factors.
Climate Monitoring and Research
Weather gizmos contribute significantly to climate monitoring and research. Long-term weather data collected from weather gizmos helps scientists track climate patterns, identify trends, and study the impact of human activities on the environment. This information is crucial for developing climate models, predicting future climate scenarios, and formulating mitigation and adaptation strategies.
4. Data Interpretation and Analysis
Interpreting and analyzing data from weather gizmos involves a structured approach to extract meaningful insights and make informed decisions.
Methods of Data Interpretation
The interpretation of data collected from weather gizmos can be done using various methods, including:
- Graphical Representation:Data is visualized using charts, graphs, and plots to identify patterns, trends, and relationships.
- Statistical Analysis:Statistical techniques, such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation, are used to summarize and analyze data.
- Time Series Analysis:Data is analyzed over time to identify trends, seasonality, and anomalies.
Importance of Calibration and Maintenance
To ensure accurate data collection, it is crucial to calibrate and maintain weather gizmos regularly. Calibration involves adjusting the device to align its readings with known standards, while maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Steps Involved in Data Analysis
Data analysis typically involves the following steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Gathering data from weather gizmos using appropriate methods and sensors. |
| Data Processing | Cleaning, filtering, and transforming data to prepare it for analysis. |
| Data Visualization | Creating visual representations of data to facilitate interpretation and identify patterns. |
Limitations and Considerations: Gizmos Observing Weather Answer Key
Weather gizmos, while valuable tools for weather observations, have certain limitations and potential sources of error that users should be aware of. Understanding these limitations can help ensure accurate readings and reliable data interpretation.
Factors that can affect the accuracy of weather gizmo readings include environmental conditions and user technique. Environmental factors such as temperature extremes, precipitation, and strong winds can impact the performance and reliability of the gizmo. Additionally, user technique, including proper calibration, placement, and data collection methods, can also influence the accuracy of the readings.
Recommendations for Effective Use
- Calibration:Ensure the weather gizmo is properly calibrated according to the manufacturer’s instructions before use.
- Placement:Choose a suitable location for the gizmo, away from obstructions and sources of interference.
- Data Collection:Follow recommended data collection protocols, including the frequency and duration of measurements.
- Environmental Conditions:Be aware of environmental conditions that may affect the accuracy of the readings, such as extreme temperatures or precipitation.
- User Technique:Use proper handling and data collection techniques to minimize user-induced errors.
Common Queries
What are the most common types of weather gizmos?
Thermometer, barometer, anemometer, rain gauge, and hygrometer are among the most widely used weather gizmos.
How do weather gizmos contribute to weather forecasting?
Weather gizmos provide real-time data on atmospheric conditions, which meteorologists use to create weather forecasts and predict future weather patterns.
What factors can affect the accuracy of weather gizmo readings?
Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, as well as user technique, can influence the accuracy of weather gizmo readings.